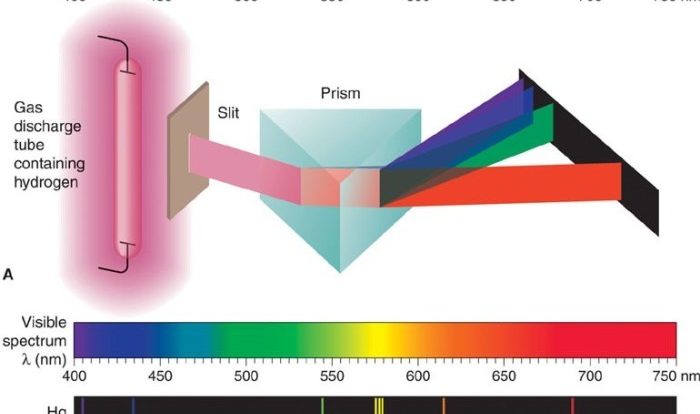
Student exploration covalent bonds answer key unlocks the intricacies of covalent bond formation, properties, and applications. Delve into the fascinating realm of chemical bonding, where atoms forge enduring connections, shaping the molecular world we inhabit.
Covalent bonds, the cornerstone of countless substances, dictate the physical and chemical properties that govern our existence. From the simplest molecules to the most complex biomolecules, covalent bonds orchestrate the symphony of life.
Covalent Bond Formation
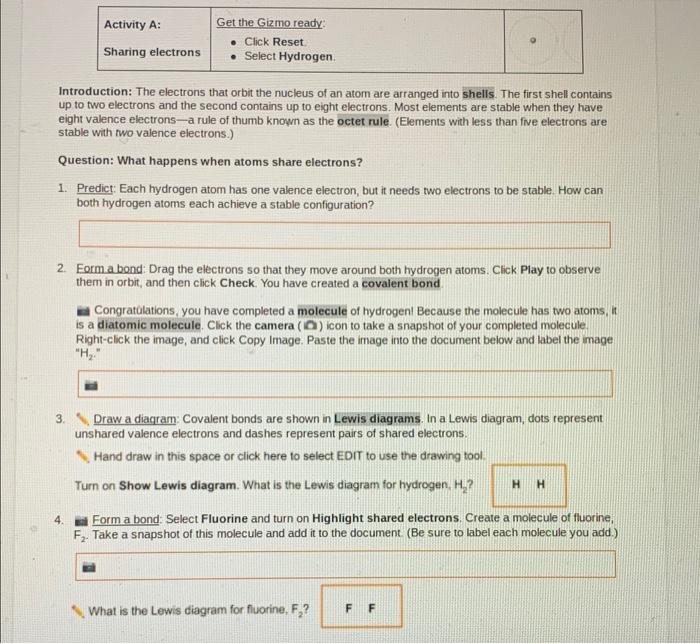
Covalent bond formation occurs when atoms share one or more pairs of electrons to achieve a more stable electron configuration. This sharing results in the formation of a molecular orbital that encompasses the nuclei of the bonded atoms.
Role of Electronegativity
Electronegativity, a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons, plays a crucial role in covalent bond formation. Atoms with high electronegativity, such as fluorine and oxygen, have a strong attraction for electrons and tend to draw them towards themselves.
This results in the formation of polar covalent bonds, where one atom has a partial positive charge and the other a partial negative charge.
In contrast, atoms with similar electronegativity, such as hydrogen and carbon, share electrons more evenly, forming nonpolar covalent bonds.
Properties of Covalent Compounds: Student Exploration Covalent Bonds Answer Key
Covalent compounds exhibit distinct physical and chemical properties compared to ionic compounds:
Physical Properties, Student exploration covalent bonds answer key
- Generally low melting and boiling points due to weak intermolecular forces
- Exist as gases, liquids, or solids at room temperature
- Poor conductors of electricity and heat
Chemical Properties
- React through covalent bond formation or breaking
- Tend to be less reactive than ionic compounds
- Can exhibit a wide range of polarities
Polarity of Covalent Bonds
The polarity of covalent bonds affects the properties of covalent compounds:
- Polar covalent bonds create molecular dipoles, resulting in dipole-dipole interactions
- Polar covalent compounds have higher melting and boiling points compared to nonpolar compounds
- Polar covalent compounds can dissolve in polar solvents
Covalent Bond Models
Lewis Dot Structure Model
The Lewis dot structure model represents covalent bonds as pairs of dots between atoms. Each dot represents a shared electron pair.
Hybridization of Atomic Orbitals
Hybridization of atomic orbitals occurs when atomic orbitals combine to form new hybrid orbitals with different shapes and energies. This hybridization enables the formation of covalent bonds with specific geometries.
Molecular Orbital Theory
Molecular orbital theory describes covalent bonds as the overlap of atomic orbitals, forming molecular orbitals that encompass the nuclei of the bonded atoms. This theory provides a more accurate understanding of bond strength and molecular properties.
Applications of Covalent Bonds
Covalent bonds play a vital role in various aspects of everyday life and science:
Everyday Life
- Water, the basis of life, is a covalent compound
- Organic compounds, such as fuels and plastics, are held together by covalent bonds
Biological Systems
- DNA and RNA, the blueprints of life, consist of nucleotides linked by covalent bonds
- Proteins, essential for life processes, are composed of amino acids joined by covalent bonds
Nanotechnology
- Carbon nanotubes and graphene, promising materials for electronics and composites, are formed by covalent bonds
- Covalent bonding is used to create nanostructures with tailored properties
Question & Answer Hub
What is the process of covalent bond formation?
Covalent bond formation occurs when two atoms share one or more pairs of electrons, creating a strong electrostatic attraction that holds them together.
How does electronegativity influence covalent bond formation?
Electronegativity, a measure of an atom’s ability to attract electrons, determines the polarity of covalent bonds. The greater the difference in electronegativity between two atoms, the more polar the bond.
What are the key differences between covalent and ionic compounds?
Covalent compounds are formed by the sharing of electrons, while ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons. Covalent compounds tend to be molecular, while ionic compounds are typically crystalline.