Beginning with organelles in eukaryotic cells pogil answer key, this article delves into the intricate world of eukaryotic cells, exploring the diverse organelles that orchestrate their remarkable functions. From the nucleus, the control center of the cell, to the mitochondria, the powerhouses of cellular energy, this guide unravels the fascinating interplay between these organelles, providing a comprehensive understanding of their essential roles in cellular life.
As we embark on this journey, we will uncover the intricate structures and specialized functions of each organelle, deciphering how they work together to maintain cellular homeostasis, facilitate growth, and ensure the proper functioning of eukaryotic organisms. Along the way, we will encounter the endoplasmic reticulum, a bustling hub for protein synthesis and modification, and the Golgi apparatus, a master sorter and modifier of cellular products.
Organelles in Eukaryotic Cells: An Overview: Organelles In Eukaryotic Cells Pogil Answer Key
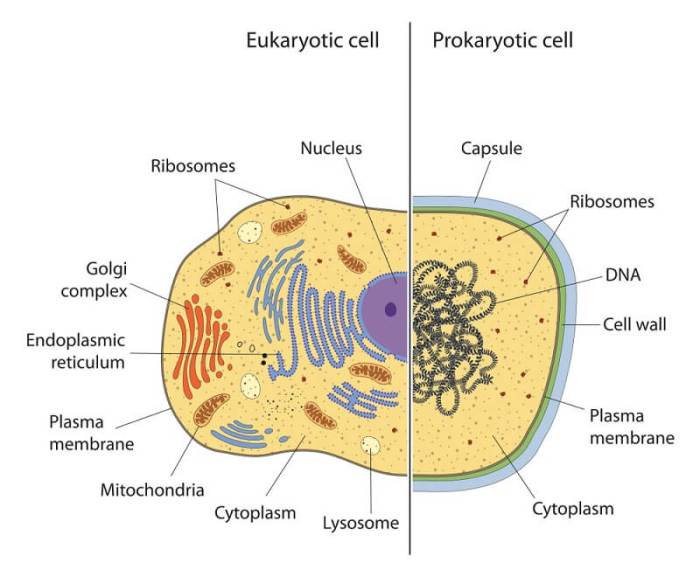
Eukaryotic cells are distinct from prokaryotic cells due to their complex organization and the presence of membrane-bound organelles. These organelles carry out specific functions essential for cell survival and function. Here is a comprehensive list of organelles found in eukaryotic cells:
- Nucleus
- Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
- Golgi apparatus
- Mitochondria
- Chloroplasts
- Ribosomes
- Lysosomes
- Peroxisomes
- Vacuoles
- Centrosome
- Microtubules
- Microfilaments
Functions and Structures of Key Organelles, Organelles in eukaryotic cells pogil answer key
NucleusThe nucleus is the control center of the cell, containing the cell’s genetic material (DNA). It is enclosed by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which contains nuclear pores that allow the exchange of materials between the nucleus and cytoplasm.
The nucleolus, a dense structure within the nucleus, is responsible for ribosome synthesis. Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)The ER is a network of interconnected membranes that extends throughout the cytoplasm. It plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and modification. The rough ER is studded with ribosomes, where protein synthesis occurs, while the smooth ER is involved in lipid metabolism and detoxification.
Golgi ApparatusThe Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranes that receives proteins from the ER. It sorts, modifies, and packages proteins for secretion or distribution to other organelles within the cell.
Questions and Answers
What is the function of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
The nucleus serves as the control center of the cell, housing the cell’s genetic material (DNA) and directing cellular activities.
What is the role of the endoplasmic reticulum in protein synthesis?
The endoplasmic reticulum is responsible for synthesizing, folding, and modifying proteins, ensuring their proper structure and function.
How do mitochondria contribute to cellular energy production?
Mitochondria are the powerhouses of the cell, generating most of the cell’s energy through cellular respiration.

