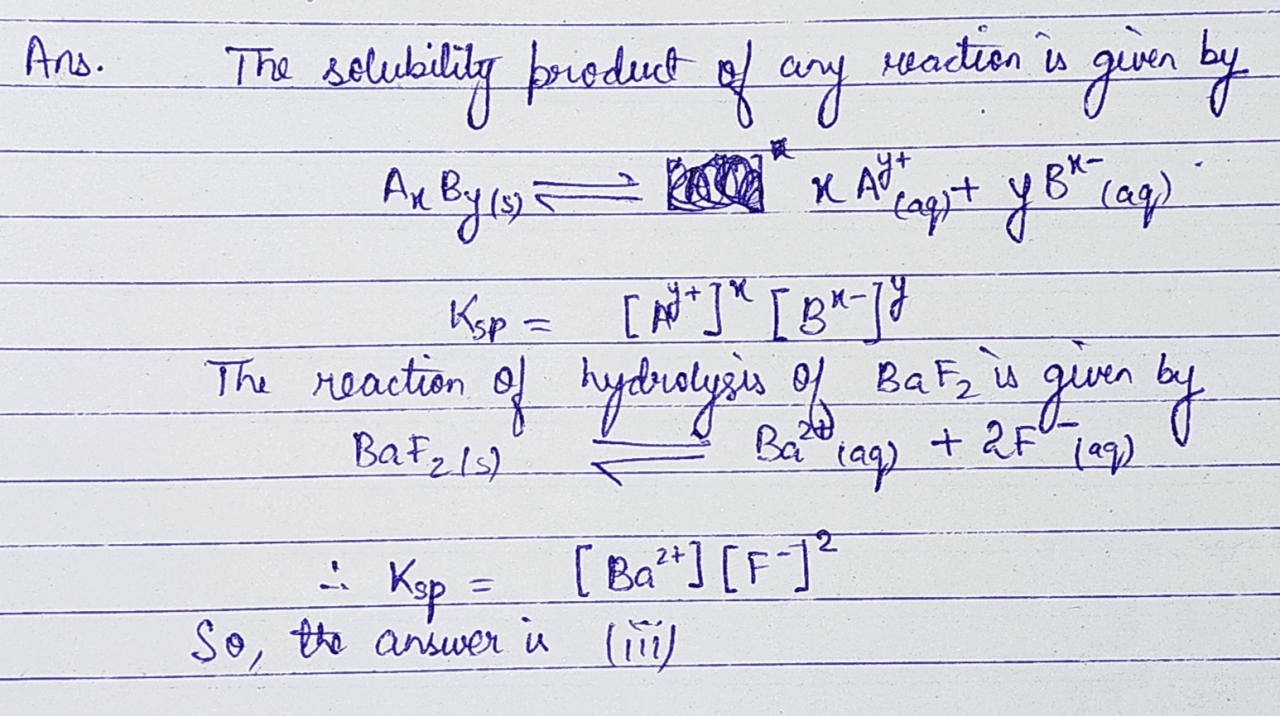Give the expression for the solubility product constant for BaF2, a crucial concept in chemistry, which plays a pivotal role in understanding the behavior of ionic compounds in aqueous solutions. This constant quantifies the extent to which a sparingly soluble ionic compound dissolves in water, providing valuable insights into the equilibrium between the solid and dissolved phases.
The solubility product constant, denoted as Ksp, is a quantitative measure of the solubility of a sparingly soluble ionic compound. It is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the constituent ions in a saturated solution, each raised to the power of their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation for the dissolution process.
For BaF2, the dissolution equation is:
BaF2(s) ⇌ Ba2+(aq) + 2F-(aq)
Accordingly, the solubility product constant for BaF2 is expressed as:
Ksp = [Ba2+][F-]^2
where [Ba2+] and [F-] represent the molar concentrations of barium and fluoride ions in the saturated solution, respectively.
Solubility Product Constant: Give The Expression For The Solubility Product Constant For Baf2
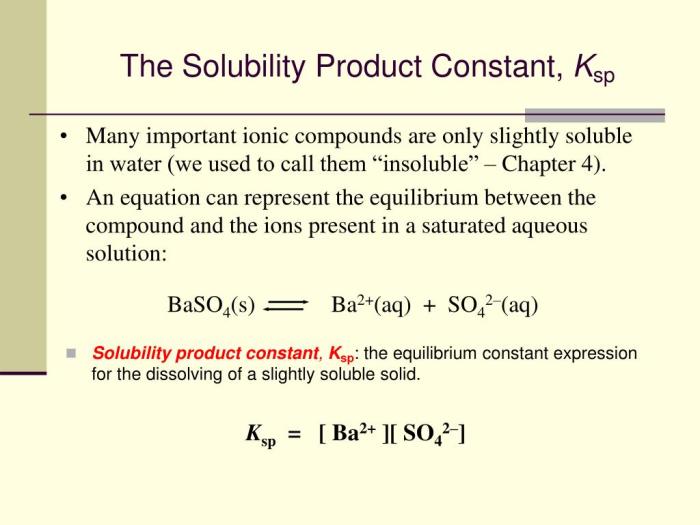
The solubility product constant (Ksp) is an equilibrium constant that describes the solubility of a sparingly soluble ionic compound in water. It is defined as the product of the concentrations of the constituent ions of the compound raised to their respective stoichiometric coefficients in the equilibrium equation.
Ksp is an important parameter in understanding chemical reactions involving precipitation, dissolution, and complexation. It allows us to predict the solubility of ionic compounds, design precipitation reactions, and study the effects of various factors on the solubility of compounds.
Solubility Product Constant for BaF2
The solubility product constant for BaF2 is defined as the product of the concentrations of Ba2+ and F- ions in a saturated solution of BaF2.
The chemical equation for the dissolution of BaF2 in water is:
BaF2(s) <=> Ba2+(aq) + 2F-(aq)
At equilibrium, the Ksp for BaF2 is given by:
Ksp = [Ba2+][F-]2
The Ksp value for BaF2 is 1.7 x 10^-6, which indicates that BaF2 is a sparingly soluble compound.
Factors Affecting the Solubility Product Constant, Give the expression for the solubility product constant for baf2
The solubility product constant of an ionic compound can be affected by several factors:
- Temperature:Ksp generally increases with increasing temperature, as higher temperatures favor the dissolution of ionic compounds.
- Ionic Strength:Ksp can decrease with increasing ionic strength, as the presence of other ions in solution can compete with the ions of the sparingly soluble compound for solvation.
- Complexation:The formation of complexes between the ions of the sparingly soluble compound and other ions in solution can reduce the concentration of free ions, thereby decreasing the Ksp.
Applications of the Solubility Product Constant
The solubility product constant has numerous applications in chemistry:
- Predicting Solubility:Ksp can be used to predict the solubility of ionic compounds in water. By comparing the Ksp value with the ion product (IP) of the compound, we can determine whether the compound will precipitate or remain dissolved.
- Designing Precipitation Reactions:Ksp can be used to design precipitation reactions by selecting reactants that have a low Ksp value. This ensures that the precipitate will form and remain insoluble.
- Environmental Chemistry:Ksp is used in environmental chemistry to study the solubility and speciation of ionic compounds in natural waters. This information is crucial for understanding the fate and transport of contaminants in the environment.
FAQ Insights
What is the significance of the solubility product constant?
The solubility product constant provides a quantitative measure of the solubility of a sparingly soluble ionic compound in water. It helps predict the extent to which the compound will dissolve and establish equilibrium between the solid and dissolved phases.
How can the solubility product constant be used to design precipitation reactions?
By manipulating the concentrations of the constituent ions in a solution, the solubility product constant can be used to control the precipitation of a desired ionic compound. This principle finds applications in analytical chemistry and various industrial processes.