We encode implicit memories by means of a complex interplay between the hippocampus and other brain regions. These memories, which encompass procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning, are crucial for everyday functioning and skill acquisition. Understanding the encoding processes of implicit memories provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of our cognitive system.
Implicit memories are distinct from explicit memories, which require conscious recollection. The encoding of implicit memories involves the formation of neural connections that are strengthened through repetition and practice. The hippocampus, a brain region essential for memory formation, plays a central role in the initial encoding of implicit memories.
However, as these memories become more ingrained, they are gradually transferred to other brain regions, such as the striatum and cerebellum, for long-term storage and retrieval.
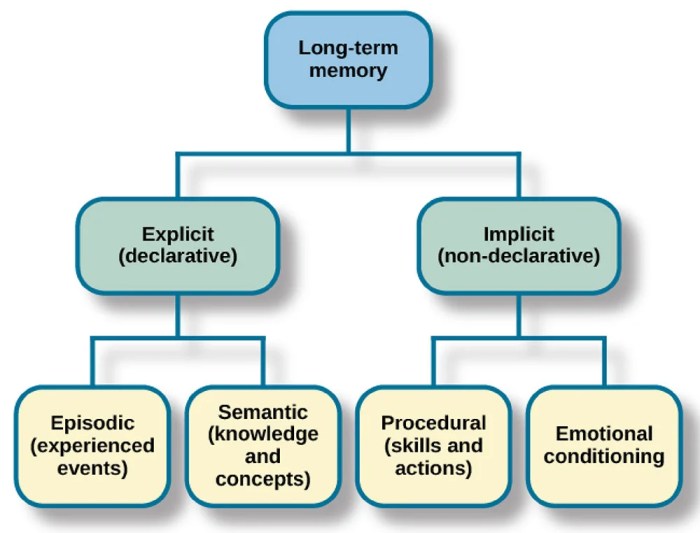
Types of Implicit Memories
Implicit memories are memories that are acquired and used unconsciously. They are different from explicit memories, which are memories that can be consciously recalled and described. There are three main types of implicit memories: procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning.
Procedural Memory
Procedural memory is the memory for how to perform skills and procedures. It is acquired through practice and repetition. Examples of procedural memories include riding a bike, playing a musical instrument, and typing.
Priming
Priming is the process by which exposure to a stimulus makes a subsequent exposure to the same or a related stimulus more likely to be recognized or recalled. Priming can be caused by a variety of stimuli, including words, pictures, and objects.
Classical Conditioning
Classical conditioning is a type of learning in which a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus. The neutral stimulus then elicits a response that is normally elicited by the meaningful stimulus. An example of classical conditioning is the salivation that occurs in response to the sound of a bell in Pavlov’s dogs.
Encoding Processes for Implicit Memories
The encoding of implicit memories is thought to involve the hippocampus and other brain regions. The hippocampus is a brain structure that is involved in memory formation. It is thought to play a role in the encoding of both explicit and implicit memories.
However, the encoding of implicit memories is thought to be more automatic and less dependent on the hippocampus than the encoding of explicit memories.The mechanisms by which implicit memories are formed and stored are not fully understood. However, it is thought that implicit memories are stored in a distributed fashion throughout the brain.
This means that there is no single brain region that is responsible for storing implicit memories.The encoding processes for implicit memories are different from the encoding processes for explicit memories. Implicit memories are typically encoded without conscious awareness. In contrast, explicit memories are typically encoded with conscious awareness.
Methods for Studying Implicit Memories

There are a variety of methods that can be used to study implicit memories. These methods include behavioral tasks, neuroimaging, and electrophysiological recordings.
Behavioral Tasks
Behavioral tasks are tasks that are designed to measure implicit memory. These tasks can be used to measure a variety of implicit memory phenomena, such as priming and classical conditioning.
Neuroimaging, We encode implicit memories by means of
Neuroimaging techniques, such as fMRI and PET, can be used to study the brain regions that are involved in implicit memory. These techniques can be used to identify the brain regions that are activated during the encoding and retrieval of implicit memories.
Electrophysiological Recordings
Electrophysiological recordings can be used to study the electrical activity of the brain during the encoding and retrieval of implicit memories. These recordings can be used to identify the neural mechanisms that are involved in implicit memory.
Examples of Implicit Memory: We Encode Implicit Memories By Means Of
Implicit memories are used in a variety of everyday situations. For example, we use implicit memories to:* Ride a bike
- Play a musical instrument
- Type
- Drive a car
- Recognize faces
- Remember how to perform a skill
Implicit memories are also important for skill acquisition and habit formation. For example, we learn how to ride a bike through practice and repetition. This practice and repetition leads to the formation of an implicit memory for how to ride a bike.
This implicit memory allows us to ride a bike without having to consciously think about how to do it.
User Queries
What are the different types of implicit memories?
Implicit memories include procedural memory, priming, and classical conditioning.
How does the hippocampus contribute to the encoding of implicit memories?
The hippocampus plays a central role in the initial encoding of implicit memories, particularly in the formation of new neural connections.
What is the difference between implicit and explicit memories?
Implicit memories are formed and retrieved unconsciously, while explicit memories require conscious recollection.