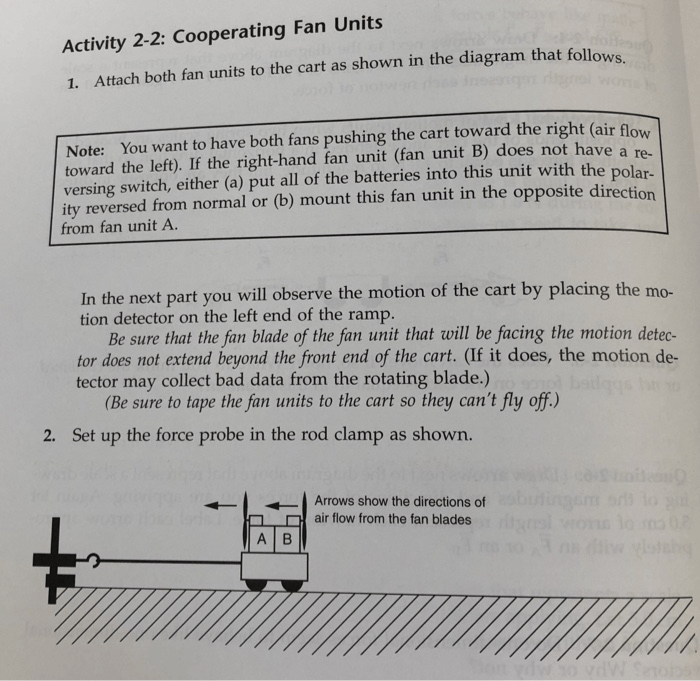
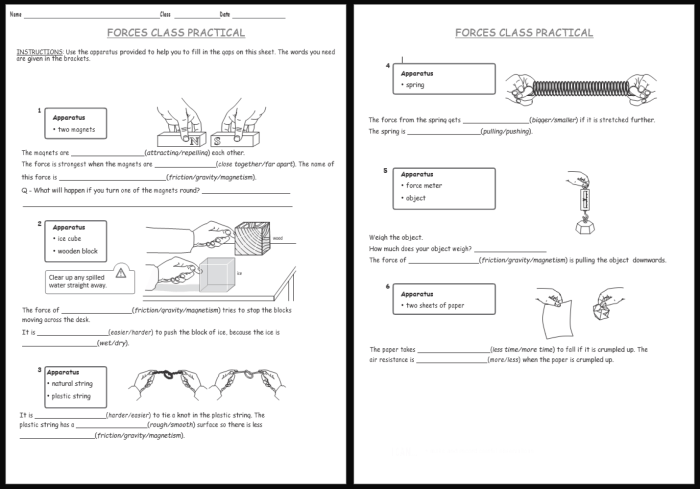
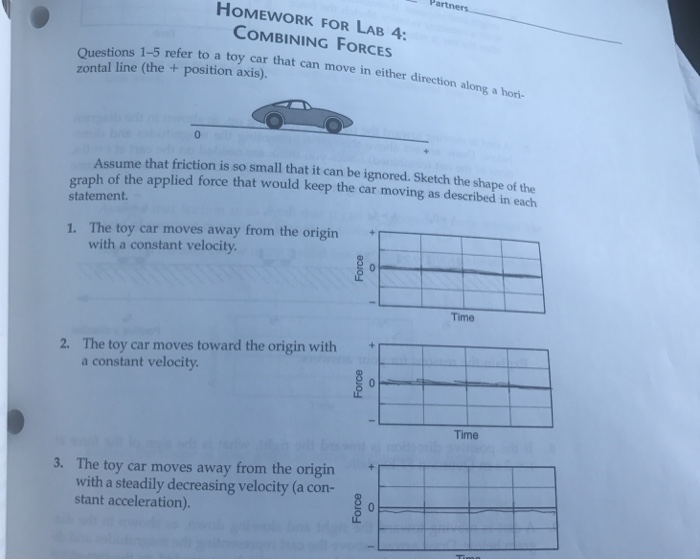
Homework for lab 4 combining forces – Homework for Lab 4: Combining Forces embarks on an academic journey, delving into the intricate world of forces and their manipulation in laboratory settings. This guide provides a comprehensive overview of the forces involved, methods for combining them, applications in various fields, and essential safety considerations.
Through a blend of theoretical explanations and practical examples, this guide empowers readers with the knowledge and skills necessary to harness the power of combined forces for effective laboratory practices.
Forces Involved in Combining
Combining lab samples often involves manipulating various forces to achieve the desired outcome. These forces can be categorized into three main types:
- Mechanical forces: These include forces applied through physical contact, such as pressure, shear, and impact.
- Chemical forces: These involve interactions between molecules, such as covalent bonds, ionic bonds, and hydrogen bonds.
- Biological forces: These encompass interactions between living organisms or their components, such as electrostatic interactions, enzyme-substrate binding, and immune responses.
The specific forces involved in combining lab samples depend on the nature of the samples and the desired outcome. For example, mechanical forces may be used to crush or grind solids, while chemical forces may be employed to dissolve or precipitate substances.
Biological forces may be utilized to separate cells or promote cell growth.
Methods for Combining Forces, Homework for lab 4 combining forces
There are several methods used to combine forces in lab settings, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
- Direct combination: This involves applying forces directly to the samples, such as by pressing, grinding, or mixing.
- Indirect combination: This involves using an intermediary device or tool to transmit forces to the samples, such as a centrifuge or a sonicator.
- Sequential combination: This involves applying forces in a specific sequence, such as first grinding the samples and then mixing them.
The choice of method depends on factors such as the nature of the samples, the desired outcome, and the available equipment.
Applications of Combining Forces
Combining forces is a versatile technique with numerous applications in laboratory settings:
- Sample preparation: Combining forces can be used to crush, grind, dissolve, or precipitate samples, facilitating further analysis.
- Cell separation: Combining forces can be used to separate cells based on size, density, or other properties.
- Chemical reactions: Combining forces can be used to promote chemical reactions by increasing the surface area of reactants or breaking down molecular bonds.
- Material synthesis: Combining forces can be used to create new materials with desired properties, such as strength, durability, or biocompatibility.
Question Bank: Homework For Lab 4 Combining Forces
What are the primary forces involved in combining lab samples?
The primary forces involved are electrostatic forces, gravitational forces, and van der Waals forces.
How can forces be manipulated to optimize combining?
Forces can be manipulated by controlling factors such as temperature, pressure, and surface properties.
What are some common troubleshooting issues when combining forces?
Common issues include incomplete mixing, uneven distribution of forces, and sample contamination. Troubleshooting involves identifying the root cause and implementing appropriate solutions.