Embark on a captivating journey into the atomic structure worksheet 2 answer key, where the fundamental building blocks of matter are unveiled. This comprehensive guide illuminates the intricacies of atomic structure, empowering you with a deeper understanding of the world around us.
Delve into the fascinating realm of protons, neutrons, and electrons, exploring their arrangement within the atom’s nucleus and electron shells. Witness the intricate dance of electrons as they occupy distinct energy levels and orbitals, shaping the chemical properties of elements.
Atomic Structure: Atomic Structure Worksheet 2 Answer Key
Atoms, the fundamental building blocks of matter, are composed of three subatomic particles: protons, neutrons, and electrons. Protons and neutrons reside in the nucleus at the center of the atom, while electrons orbit the nucleus in shells.
The number of protons in an atom determines its atomic number and element type. The number of neutrons determines the isotope of an element. Electrons, on the other hand, are responsible for the atom’s chemical properties.
Electron Configuration, Atomic structure worksheet 2 answer key
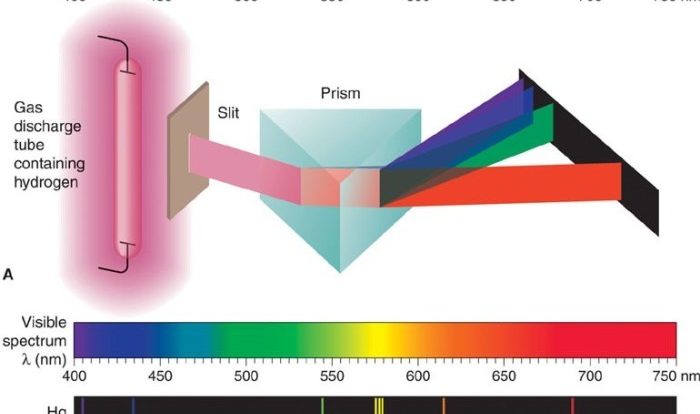
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons in different energy levels and orbitals around the nucleus. The energy levels are designated as n = 1, 2, 3, … and the orbitals within each energy level are labeled as s, p, d, f.
Electrons fill orbitals in a specific order, following the Aufbau principle and Hund’s rule.
Periodic Trends
Periodic trends describe the systematic variation in atomic properties as we move across and down the periodic table. These trends include atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. They can be explained based on the increasing atomic number and the effective nuclear charge experienced by electrons.
Chemical Bonding
Chemical bonding involves the interaction between atoms to form molecules and compounds. The type of bond formed depends on the electronic configuration of the atoms involved. There are three main types of chemical bonds: ionic, covalent, and metallic.
Applications of Atomic Structure
An understanding of atomic structure has wide-ranging applications in various fields:
- Chemistry:Predicting and explaining chemical reactions, designing new materials
- Materials science:Developing advanced materials with tailored properties
- Nuclear physics:Understanding nuclear reactions and energy production
FAQ Summary
What is the significance of electron configuration?
Electron configuration plays a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of elements. It influences their reactivity, bonding behavior, and position in the periodic table.
How do periodic trends help us understand atomic properties?
Periodic trends reveal patterns in atomic properties across the periodic table. These trends, such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity, can be explained based on the atomic structure of elements.
What are the different types of chemical bonds?
The three main types of chemical bonds are ionic, covalent, and metallic bonds. Each type of bond involves a distinct mechanism of electron sharing or transfer, resulting in different properties and characteristics.