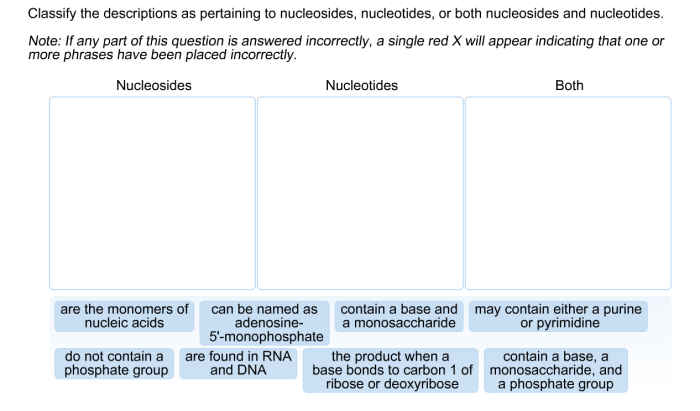
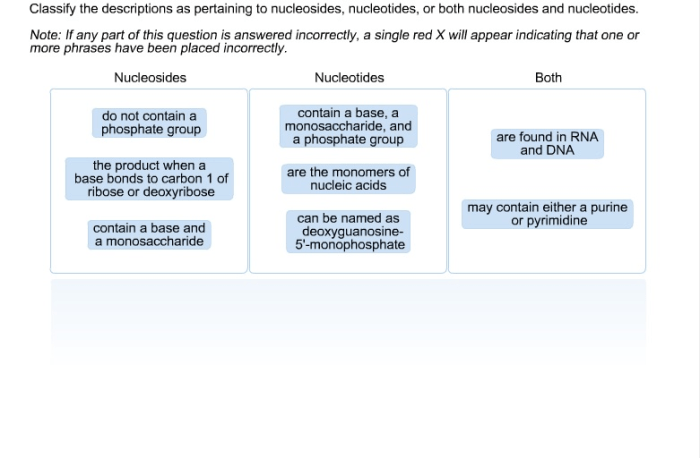
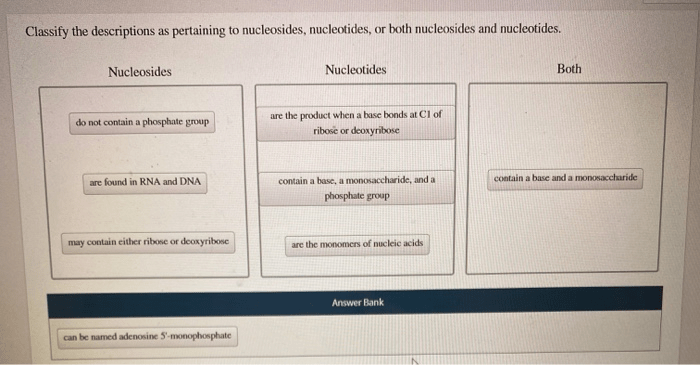
Classify the descriptions as pertaining to nucleosides – Delving into the realm of nucleosides, this discourse embarks on an illuminating journey to classify these fundamental molecular entities. Nucleosides, the precursors to nucleotides, play a pivotal role in the intricate tapestry of biological systems, serving as the building blocks for RNA and DNA.
As we unravel the structural characteristics and diverse functions of nucleosides, we gain a deeper appreciation for their significance in cellular processes and genetic information transfer.
This comprehensive exploration will delve into the chemical composition of nucleosides, categorizing them based on their structural features. We will examine the distinct classes of nucleosides, including ribonucleosides and deoxyribonucleosides, highlighting their unique properties and biological significance. Furthermore, we will illuminate the multifaceted roles of nucleosides in cellular metabolism, energy production, and the transmission of genetic information.
1. Nucleosides
Definition and Structure
Nucleosides are organic molecules that play a crucial role in various biological processes. They consist of two components: a nitrogenous base and a pentose sugar molecule.
The nitrogenous bases found in nucleosides are either purines (adenine and guanine) or pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine, and uracil). The pentose sugar molecule is either ribose (in ribonucleosides) or deoxyribose (in deoxyribonucleosides).
Examples of nucleosides include adenosine, guanosine, cytidine, thymidine, and uridine.
2. Classification of Nucleosides: Classify The Descriptions As Pertaining To Nucleosides
2.1 Based on Structural Characteristics, Classify the descriptions as pertaining to nucleosides
Nucleosides can be classified based on the type of nitrogenous base they contain. Purine nucleosides contain purine bases (adenine or guanine), while pyrimidine nucleosides contain pyrimidine bases (cytosine, thymine, or uracil).
Another classification is based on the type of pentose sugar they contain. Ribonucleosides contain ribose sugar, while deoxyribonucleosides contain deoxyribose sugar.
2.2 Classification System
| Class | Nitrogenous Base | Pentose Sugar |
|---|---|---|
| Purine nucleosides | Adenine or guanine | Ribose or deoxyribose |
| Pyrimidine nucleosides | Cytosine, thymine, or uracil | Ribose or deoxyribose |
3. Functions of Nucleosides
Nucleosides play diverse roles in biological systems:
- Nucleotide synthesis:Nucleosides are the precursors for the synthesis of nucleotides, which are the building blocks of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
- RNA and DNA building blocks:Nucleosides are incorporated into RNA and DNA molecules during their synthesis.
4. Importance of Nucleosides in Biochemistry
Nucleosides are essential for various cellular processes:
- Energy metabolism:Nucleosides are involved in the production of ATP, the primary energy currency of cells.
- Genetic information transfer:Nucleosides carry genetic information in RNA and DNA molecules, enabling the transfer of genetic material from one generation to another.
Clarifying Questions
What are nucleosides?
Nucleosides are organic molecules composed of a nitrogenous base linked to a ribose or deoxyribose sugar molecule.
How are nucleosides classified?
Nucleosides are classified based on the type of sugar molecule they contain, such as ribonucleosides (containing ribose) and deoxyribonucleosides (containing deoxyribose).
What are the functions of nucleosides?
Nucleosides serve as precursors to nucleotides, which are essential for nucleotide synthesis, RNA and DNA formation, energy metabolism, and genetic information transfer.