Label the specific serous membranes and cavity of the heart – Labeling the specific serous membranes and cavity of the heart is a crucial step in understanding the intricate anatomy of this vital organ. Serous membranes, delicate tissues that line body cavities and organs, play a significant role in the smooth functioning of the heart.
The pericardium, epicardium, myocardium, and endocardium are the four serous membranes associated with the heart. Each membrane has a distinct structure and function, contributing to the overall protection and performance of the heart.
Serous Membranes of the Heart: Label The Specific Serous Membranes And Cavity Of The Heart
Serous membranes are thin, double-layered membranes that line body cavities and cover organs. They consist of a layer of mesothelium (a type of epithelium) and a layer of connective tissue. Serous membranes serve to reduce friction between organs and protect them from damage.
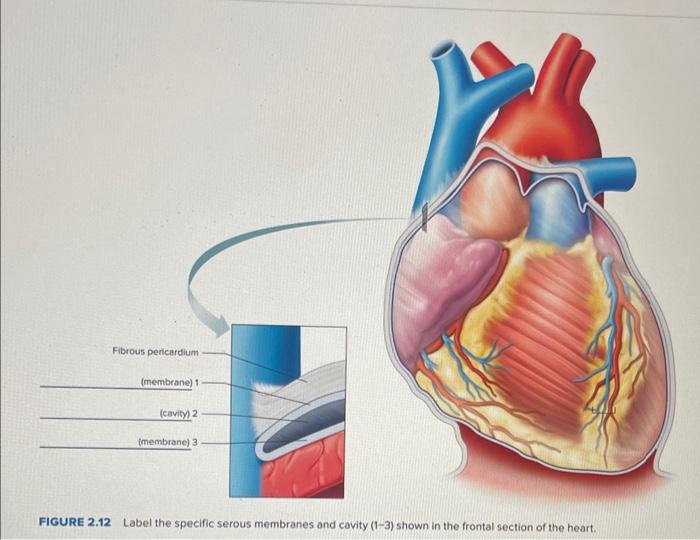
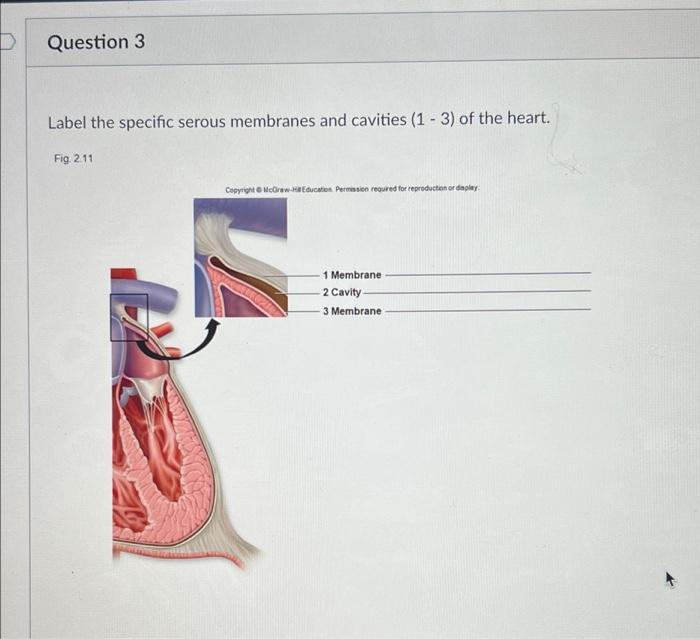
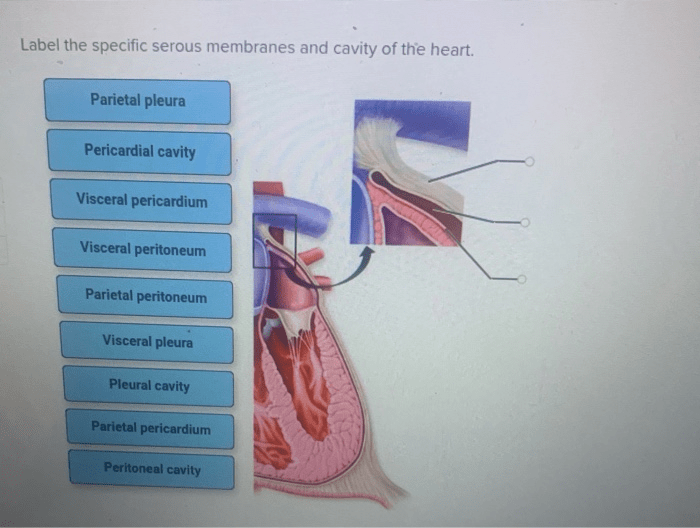
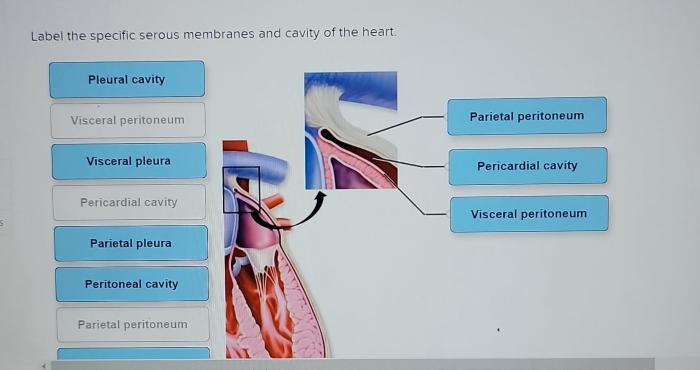
The heart is enclosed in a serous membrane called the pericardium. The pericardium consists of two layers: the visceral pericardium (epicardium) and the parietal pericardium. The visceral pericardium is attached to the surface of the heart, while the parietal pericardium lines the pericardial cavity.
The pericardial cavity is the space between the visceral and parietal pericardium. It contains a small amount of fluid that helps to lubricate the heart and reduce friction.
Epicardium
The epicardium is the visceral layer of the pericardium. It is a thin, transparent membrane that covers the surface of the heart. The epicardium is composed of mesothelium and a thin layer of connective tissue.
The epicardium serves to protect the heart from damage and infection. It also helps to anchor the heart to the surrounding structures.
Myocardium, Label the specific serous membranes and cavity of the heart
The myocardium is the middle layer of the heart. It is composed of cardiac muscle tissue. The myocardium is responsible for the pumping action of the heart.
The myocardium is divided into four chambers: the right atrium, the right ventricle, the left atrium, and the left ventricle. The atria are the receiving chambers of the heart, while the ventricles are the pumping chambers.
Endocardium
The endocardium is the innermost layer of the heart. It is a thin, smooth membrane that lines the chambers of the heart and covers the valves.
The endocardium serves to prevent blood leakage from the heart. It also helps to protect the heart from infection.
Relationship Between Serous Membranes and Cardiac Function
Serous membranes play an important role in the smooth functioning of the heart. They reduce friction between the heart and the surrounding structures, preventing damage and wear. The pericardial cavity also provides a cushion that helps to protect the heart from injury.
In addition, serous membranes help to maintain proper cardiac fluid balance. The fluid in the pericardial cavity helps to lubricate the heart and prevent it from drying out.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the function of the serous membranes associated with the heart?
Serous membranes reduce friction between organs, prevent adhesions, and maintain proper fluid balance.
What are the layers of the pericardium?
The pericardium has two layers: the fibrous pericardium and the serous pericardium.
What is the role of the epicardium?
The epicardium protects the heart from external damage and infections.